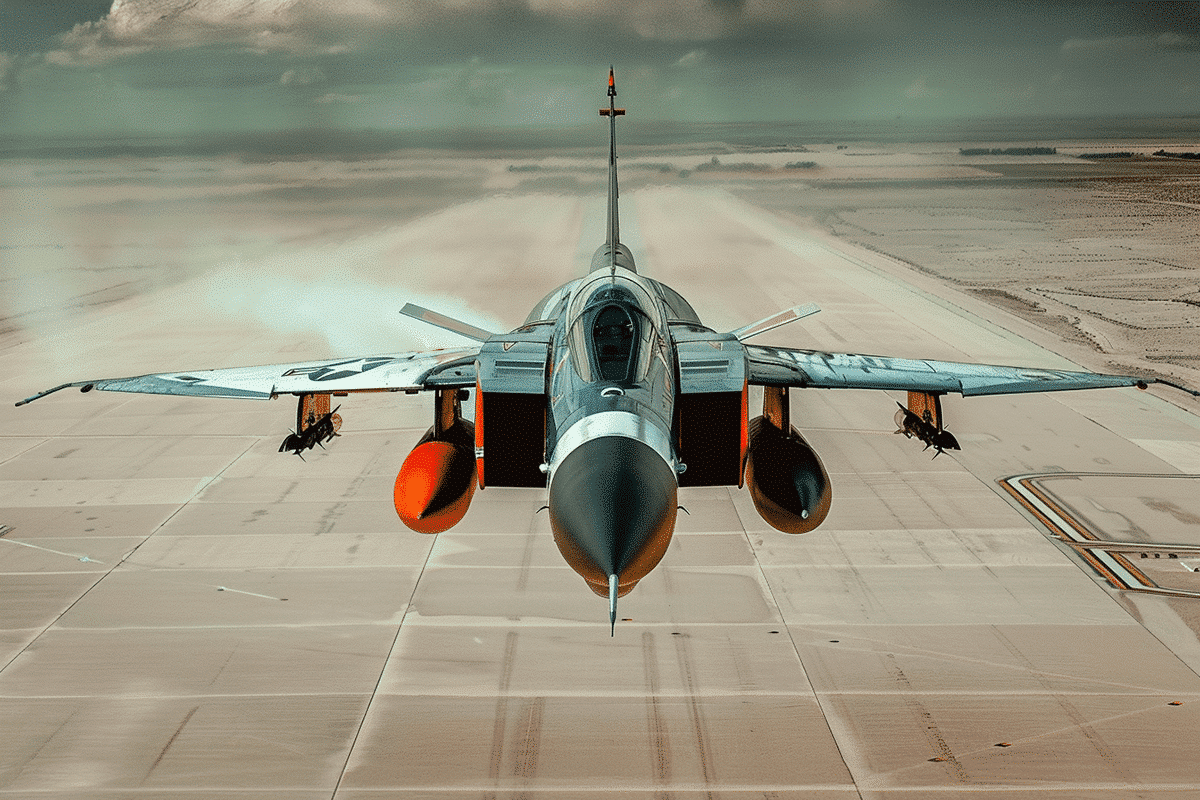
In a groundbreaking display of technological prowess, an artificial intelligence (AI)-guided fighter jet engaged in a riveting dogfighting test against a human-controlled counterpart. The duel, which occurred in September 2023, recently came to light with the release of footage by DARPA’s Air Combat Evolution program.
The remarkable footage unveils a high-speed aerial ballet as the two aircraft, one manned by a human pilot and the other autonomously guided by AI, execute a series of dynamic combat maneuvers. Zooming through the skies at a blistering pace of 1,931 kilometers per hour, the aircraft showcase their agility and precision, maneuvering into nose-to-nose dogfighting positions with astonishing finesse.
At the heart of this technological marvel is the AI-guided plane, known as the X-62A or VISTA (Variable In-flight Simulator Test Aircraft). Developed through a collaboration between Lockheed Martin Skunk Works and Calspan Corporation, this cutting-edge aircraft initially began as a simulator program designed to train pilots. However, it swiftly evolved beyond its virtual confines when, in December 2022, AI agents were entrusted with the reins of a physical aircraft in the real world.
Since then, the AI-powered aircraft has logged numerous hours of both real-world and simulated flight, honing its skills and capabilities for its ultimate mission: engaging in within-visual-range combat scenarios, commonly referred to as “dogfighting.”
The significance of this technological leap is underscored by its potential to revolutionize air combat. Colonel James Valpiani, Air Force Test Pilot School commandant, emphasizes the promise of machine learning in the perilous realm of air-to-air combat, where split-second decisions can mean the difference between victory and defeat.
Further showcasing the program’s progress is the recent flight of US Secretary of the Air Force Frank Kendall aboard the AI-guided X-62A jet on May 2, 2024. Kendall’s presence underscores the strategic imperative of integrating AI into military operations, with Kendall stressing the necessity of embracing such technology for national security.
Indeed, the advent of AI-assisted weapons holds the tantalizing prospect of enhanced accuracy, potentially minimizing collateral damage, civilian casualties, and the risk of friendly fire incidents. However, this frontier of innovation also raises a host of ethical, legal, and security concerns.
Foremost among these concerns is the question of accountability and oversight. With AI systems assuming increasingly autonomous roles in decision-making, there arises the daunting prospect of entrusting life-and-death judgments to algorithms with minimal human intervention. Critics caution against the dangers of unchecked AI proliferation, warning of the ethical quagmire posed by the deployment of what effectively amount to “killer robots.”
In response to these apprehensions, calls for stringent regulation of militarized AI have grown louder. Advocates argue that robust oversight mechanisms are imperative to safeguard against the potential perils of unrestrained AI development.
Yet, amidst these deliberations, the specter of an AI arms race looms large. With nations vying to gain an edge in the realm of autonomous warfare, the pace of technological innovation shows no signs of abating.
As the debate rages on, the intersection of AI and military technology remains a crucible of innovation and ethical introspection. In this brave new world of unmanned aerial combat, the quest for balance between technological prowess and ethical responsibility will shape the future of warfare.