Venezuela, one of Latin America’s most urbanized nations, continues to grapple with severe economic and political challenges. Known for having some of the world’s largest proven oil reserves and abundant resources such as coal, iron ore, bauxite, and gold, Venezuela has historically been a global oil exporter. However, in the 21st century, the nation has faced a steep decline due to poor economic management and fluctuating oil prices.
Economic Collapse and Humanitarian Crisis
Once a dominant oil power, Venezuela’s fortunes have changed drastically over the past two decades. Following the leadership of Hugo Chavez, who ruled from 1999 until his death in 2013, the country saw oil wealth diverted toward expansive social programs aimed at improving the quality of life for the poor. However, this heavy dependence on oil income left the country vulnerable when prices began to plummet. Chavez’s successor, Nicolas Maduro, inherited an economy in decline, and his administration has struggled to revive the nation amid ongoing crises.
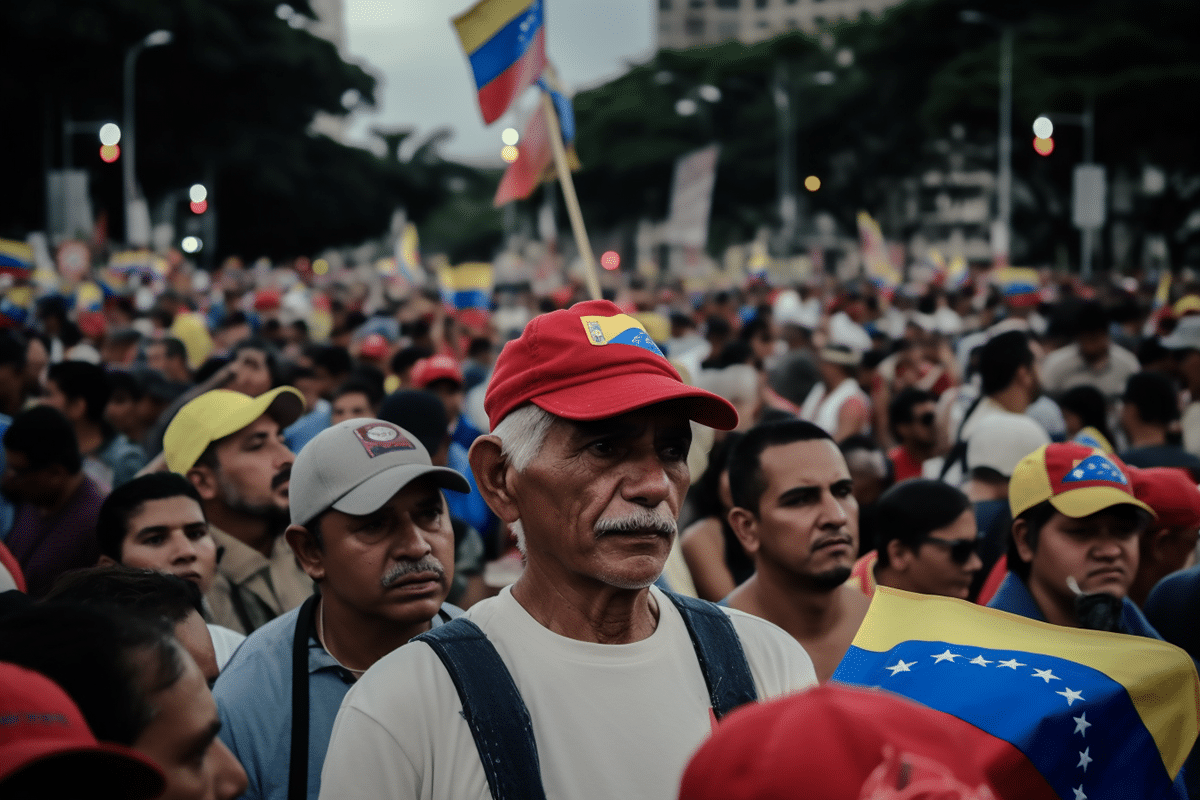
Today, Venezuela faces rampant inflation, widespread shortages of essential goods, and skyrocketing unemployment. The economic freefall has triggered a massive humanitarian crisis, with more than seven million Venezuelans fleeing the country, seeking refuge in neighboring states. As the crisis deepens, crime rates have surged, making daily life increasingly difficult for those who remain in the country.
Political Tensions and Contested Elections
Nicolas Maduro has governed Venezuela since 2013, but his leadership has been marked by intense political strife. The most recent presidential election, held in July 2024, once again placed Maduro in power. However, the opposition party has refused to accept the election results, claiming their candidate, Edmundo González, was the rightful winner. Following the vote, González fled to Spain after Venezuelan authorities issued an arrest warrant for him.
Maduro’s election victory has been met with skepticism from the international community. The United States, the European Union, and other foreign governments have refrained from recognizing Maduro’s third term, calling for transparency and detailed voting data to validate the results. While some of Maduro’s allies, including Russia, China, and Iran, have backed his government, many Western countries continue to seek a peaceful transition of power through negotiations.
This election is a continuation of Venezuela’s troubled political climate. The 2018 election was widely regarded as unfair, leading several countries, including the U.S., to recognize opposition leader Juan Guaidó as the interim president. This decision resulted in severe sanctions being imposed on Venezuela, further worsening the country’s economic struggles.
Long-Standing Border Dispute with Guyana
Venezuela’s internal turmoil is compounded by a long-standing border dispute with neighboring Guyana over the oil-rich Essequibo region. This territorial conflict dates back to 1889 when Venezuela laid claim to two-thirds of Guyana’s territory west of the Essequibo River. An international arbitration ruling in 1899 favored Guyana, but Venezuela has never accepted the decision.
In 2023, Venezuelans overwhelmingly supported their country’s claim to the Essequibo region in a national referendum. This decision also included the establishment of a new Venezuelan state in the contested area. The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has since rejected Venezuela’s argument that it is not the appropriate body to rule on the matter, and the case is now progressing through legal proceedings.
The border dispute has reignited nationalistic fervor within Venezuela, with many citizens backing the government’s stance on Essequibo. However, it also risks heightening tensions with Guyana and the broader international community, particularly as the ICJ moves closer to making a ruling.
A Nation in Transition
Despite its significant natural resources, Venezuela’s future remains uncertain. The combination of economic mismanagement, political instability, and international isolation has plunged the country into a deep crisis from which recovery seems distant. As Nicolas Maduro begins his third term amid controversy, the Venezuelan people continue to face the harsh realities of life in a country on the brink of collapse.
The ongoing border dispute with Guyana adds another layer of complexity, with potential consequences for the region’s stability. As Venezuela presses its claim to Essequibo, the international community watches closely, uncertain about how the situation will evolve.
For now, Venezuela remains a nation defined by its struggles, both internal and external. With millions of its citizens fleeing and its economy in ruins, the road to recovery will be long and fraught with challenges. However, the resilience of the Venezuelan people and their rich natural resources may yet provide a glimmer of hope for the future.