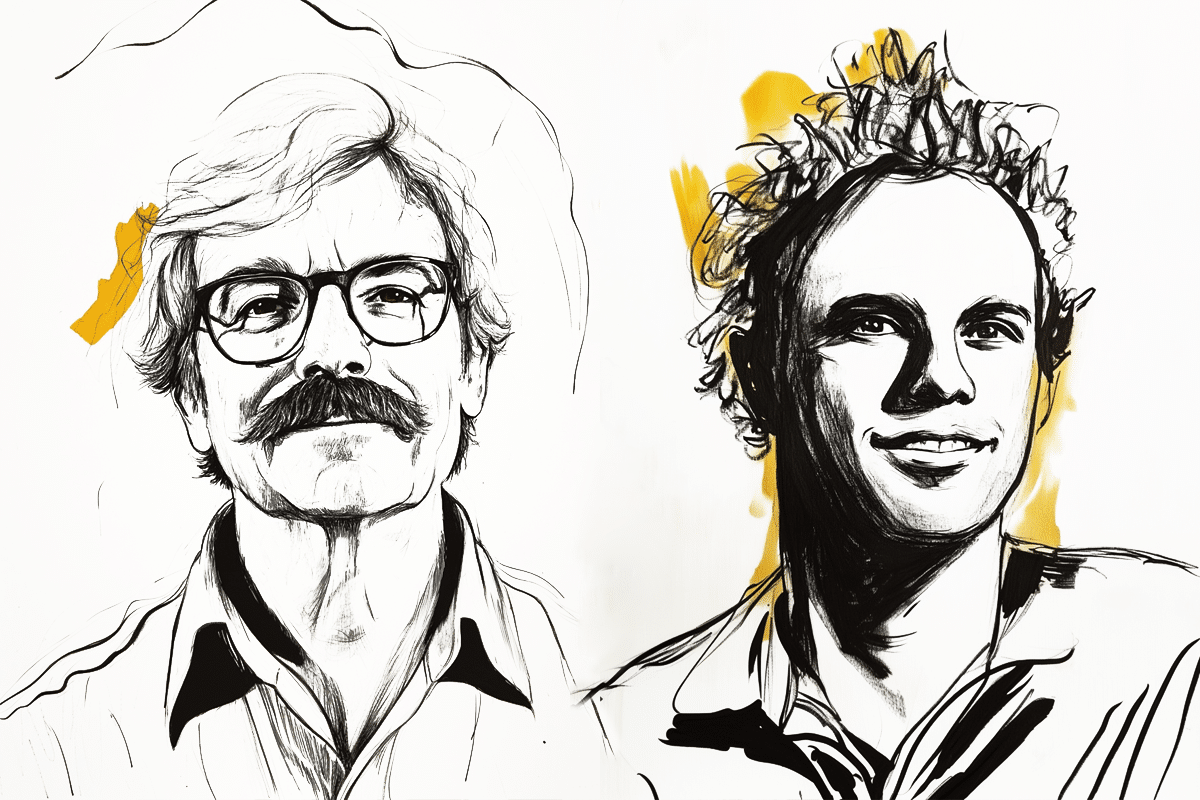
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to American scientists Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for their groundbreaking discovery of microRNA, a crucial mechanism that helps regulate gene activity in cells. This discovery has opened new possibilities for controlling how genes function, offering promising approaches for treating diseases, including cancer.
MicroRNA, tiny bits of genetic material, plays a vital role in regulating gene expression, switching critical genes on and off. Unlike RNA, which is primarily known for carrying instructions to produce proteins, microRNA acts as a regulatory tool. This mechanism helps ensure that cells develop and function correctly by controlling which genes are active at any given time.
The discovery of microRNA has reshaped scientists’ understanding of gene regulation, revealing an entirely new dimension in how organisms grow and develop. This process is not only essential for humans but for all complex life forms. By controlling the timing of genetic developments in cells, microRNA ensures that cells develop in the right sequence, contributing to proper growth and function in multicellular organisms.

A New Understanding of Gene Regulation
Ambros and Ruvkun’s research initially focused on studying gene mutations in worms, a common model in biological research. Their aim was to understand how specific genes affected the development of cells in these organisms. Through their experiments, they identified the role microRNA plays in regulating genes, allowing the fine-tuning of cell functions. This regulatory system has been evolving for hundreds of millions of years, helping organisms to adapt and survive.
The impact of their discovery extends far beyond developmental biology. MicroRNA has become an essential tool in exploring how genes contribute to diseases and how their activity can be controlled to treat these conditions. This novel principle of gene regulation provides a foundation for developing therapies targeting diseases at a genetic level, including cancer, infectious diseases, and neurological disorders.
A Path Toward New Treatments
The study of microRNA holds immense potential for medical research and drug development. MicroRNA can help scientists manipulate how genes function, offering a new way to intervene in disease processes. In cancer research, for instance, microRNA could be used to halt the activity of mutated genes that drive the growth of tumors. By delivering specific microRNAs to affected cells, researchers can potentially stop harmful genes from causing further damage.
This approach could also serve as a tool for diagnosing diseases. By tracking levels of microRNA in the body, doctors could identify the presence of certain diseases earlier, making treatment more effective. Although no drugs based on microRNA have yet been approved, ongoing research indicates that such treatments could be available within the next decade.
MicroRNA’s potential isn’t limited to cancer. Studies are also investigating its role in infectious diseases such as hepatitis and its potential application in treating neurological conditions. As more is learned about how microRNA functions in the body, the scientific community anticipates even more groundbreaking applications in healthcare.
A Transformative Moment
The recognition of Ambros and Ruvkun’s work by the Nobel committee highlights the transformative impact their discovery has had on the field of biology. The Nobel Prize, one of the most prestigious awards in science, not only recognizes the significance of microRNA but also shines a spotlight on the importance of basic research in advancing human knowledge.
For both scientists, this award represents a major milestone. Ambros, a professor of natural science at the University of Massachusetts Medical School, conducted much of his research at Harvard University. Ruvkun, a professor of genetics at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, echoed the sentiment that the Nobel Prize is a life-changing achievement.
Their discovery of microRNA underscores the value of curiosity-driven research, often funded by taxpayer money, which leads to unexpected and groundbreaking advancements.
Looking Ahead
With the Nobel Prize serving as a testament to the importance of this discovery, the potential applications of microRNA are vast. The future of medical research will likely see this small but powerful genetic material playing a critical role in developing new therapies and treatments.
The Nobel Prize in Medicine, carrying a cash award of 11 million Swedish kronor ($1 million), continues to highlight important contributions to science and health. The announcement is part of the annual series of Nobel Prize announcements, with upcoming awards in physics, chemistry, and peace to be revealed in the coming days.
MicroRNA has proven to be a key player in the future of medicine, offering scientists new ways to understand, treat, and potentially cure some of the most challenging diseases of our time. Ambros and Ruvkun’s discovery marks a new chapter in genetic research, one that promises to unlock many more secrets of life at the molecular level.